

On the periodic table of the elements, atomic radius tends to increase when moving down columns, but decrease when moving across rows (left to right). A metallic radius is one-half the distance between the nuclei of two adjacent atoms in a crystalline structure, when joined to other atoms by metallic bonds. Covalent radius is the nominal radius of the atoms of an element when covalently bound to other atoms. An ionic radius is one-half the distance between the nuclei of two ions in an ionic bond.
#HELIUM ATOM FREE#
However, this assumes the atom to exhibit a spherical shape, which is only obeyed for atoms in vacuum or free space. The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the distance out to which the electron cloud extends from the nucleus.

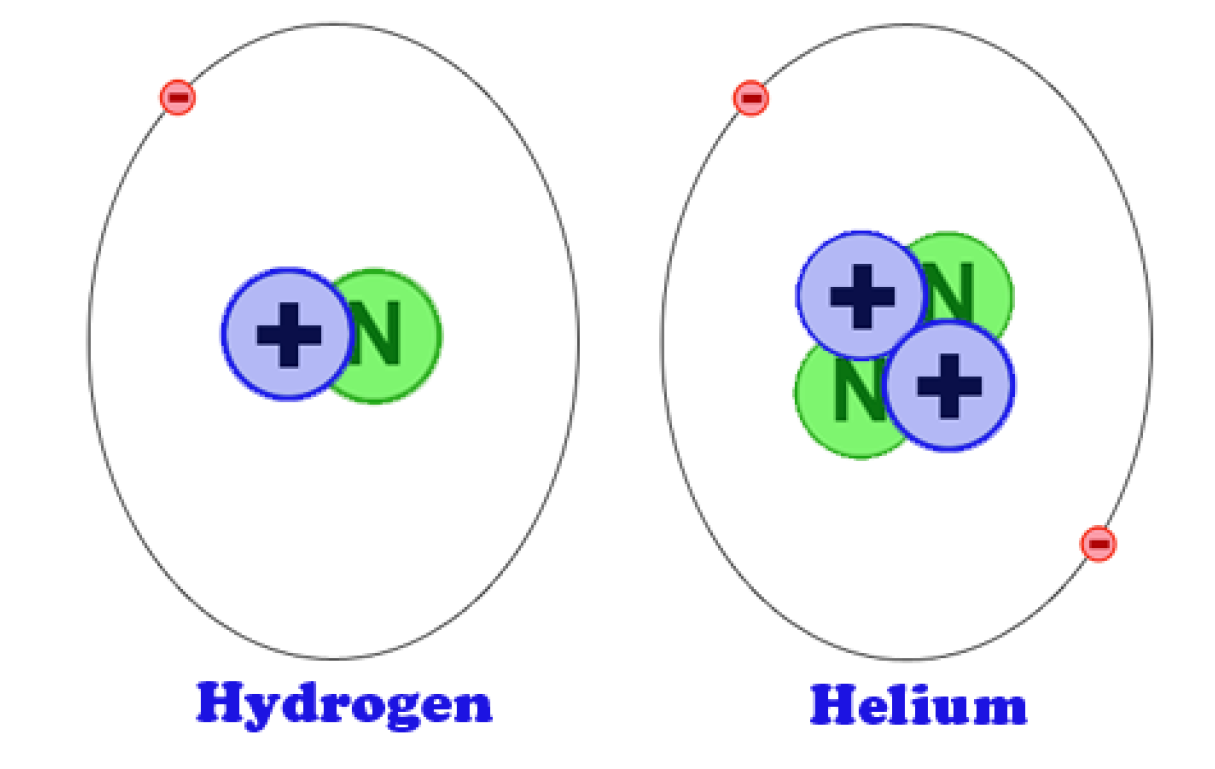
It must be noted, atoms lack a well-defined outer boundary. Sufficiently high temperatures are found in the interior of the Sun, where fusion reactions take place.The atomic radius of Helium atom is 28pm (covalent radius).
This high temperature, required because of the electric repulsion barrier to the reaction, is the main reason why it has been so difficult to make progress toward thermonuclear power generation. The approximate temperature required for the fusion reaction to proceed is very high. 4 × 10 - 23 J / K, and is the absolute or Kelvin temperature, measured from absolute zero (so that the freezing point of water is 273 K ). If a mole of hydrogen and a mole of deuterium underwent this fusion reaction, how much kinetic energy would be generated? (For comparison, around are obtained from burning a mole of gasoline.) (e) Which of the following potential energy curves in Figure 6.87 is a reasonable representation of the interaction in this fusion reaction? Why?Īs we will study later, the average kinetic energy of a gas molecule is 3 2 k b T, where is the “Boltzmann constant,” 1. (d) Kinetic energy can be used to drive motors and do other useful things. What is the net energy release, in joules and in electron volts? Note that you do get back the energy investment made in part (a).
#HELIUM ATOM PLUS#
6 × 10 - 19 J )? (b) Given the initial conditions found in part (a), what is the kinetic energy of the He 3 plus the energy of the gamma ray, in joules and in electron volts? (c) The net energy released is the kinetic energy of the He 3 plus the energy of the gamma ray found in part (b), minus the energy input that you calculated in part (a). What is the approximate initial total kinetic energy of the proton and deuteron required for the fusion reaction to proceed, in joules and electron volts ( 1 eV = 1.
The approximate radius of a proton or neutron is about 1 × 10 - 15 m. For this fusion reaction to take place, the proton and deuteron have to come close enough together to touch. (a) The strong interaction has a very short range and is essentially a contact interaction. Problems involving mass changes require many significant figures because the changes in mass are small compared to the total mass. Although in most problems you solve in this course it is adequate to use values of constants rounded to two or three significant figures, in this problem you must keep at least six significant figures throughout your calculation. 7 × 10 - 27 kg ), the mass of the deuteron is 2.0136 u, the mass of the helium-3 nucleus is 3.0155 u, and the gamma ray is massless. The mass of the proton is 1.0073 u (unified atomic mass unit, 1. This is one of the thermonuclear or fusion reactions that takes place inside a star such as our Sun. If they get close enough to make actual contact with each other, they can react to form a helium-3 nucleus and a gamma ray (a high-energy photon, which has kinetic energy but zero rest energy): H 1 + 2 H → 3 He + y An experimental apparatus shoots them toward each other (with equal and opposite momenta). A proton ( H 1 ) and a deuteron ( ( H 2 ), “heavy” hydrogen) start out far apart.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
